Aptamer Selection
Small molecule aptamer screening techniques generally include the following steps:
A. Initial library design: Build a DNA, RNA or peptide library containing a large number of random sequences that have the potential to bind to small target molecules.
B. Screening process: The main steps include target binding to the library, isolation and purification of the binding target molecule aptamer PCR amplification, iterative screening and so on. After each round of screening, the screening results can be verified and analyzed through technologies such as sequencing.
C. Optimization and validation: The selected aptamers were optimized to improve their affinity, specificity and stability. Subsequently, a series of experiments were carried out to verify its binding ability and application effect.
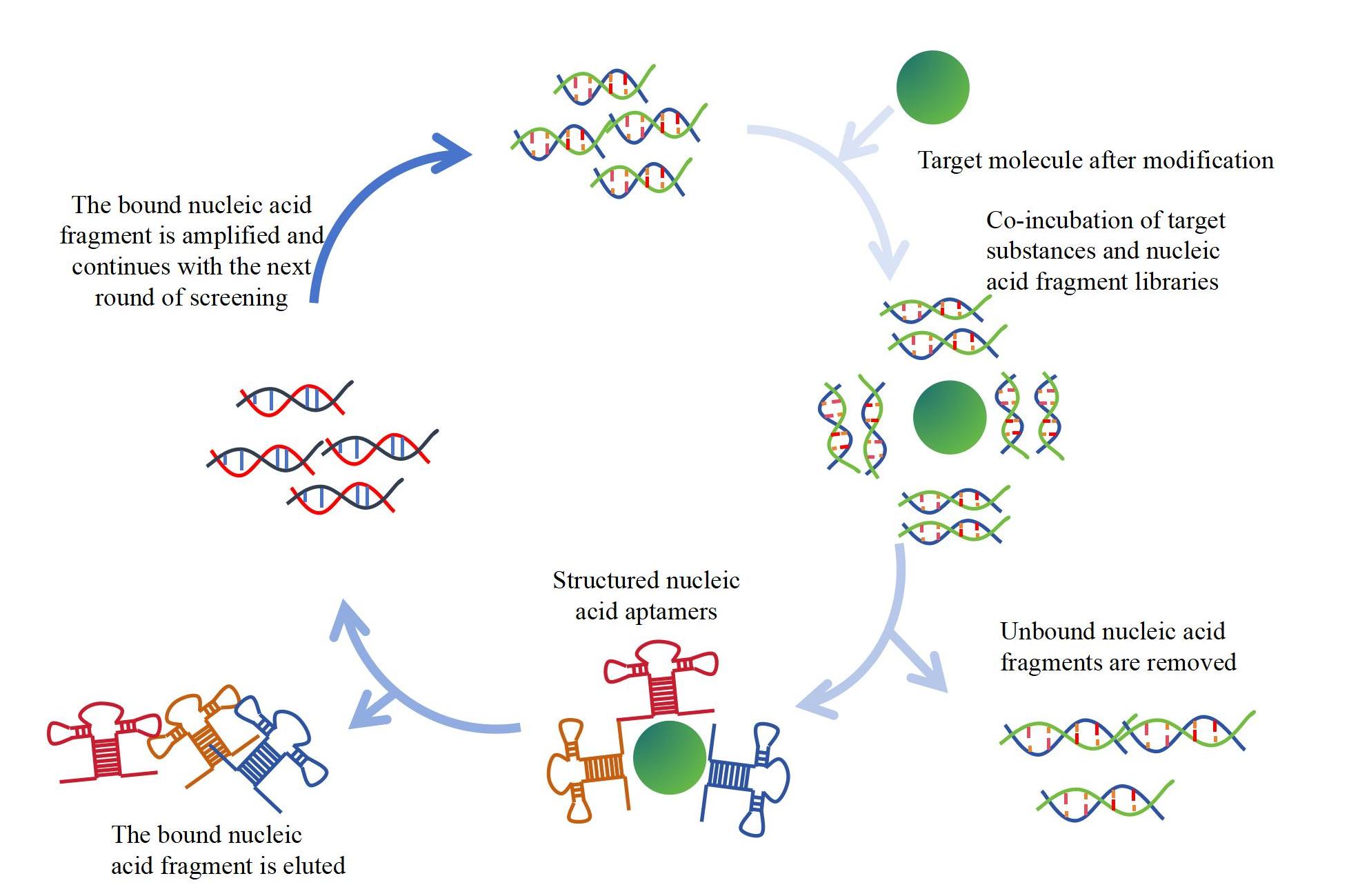
Your description accurately captures the three universal pillars of in vitro selection (SELEX). KMD Bioscience would operationalize these into a robust, client-tailored service.
Library Diversity: Construction of high-complexity synthetic libraries (typically 10^14 – 10^15 unique sequences) containing a central random region (e.g., 30-60 nucleotides) flanked by constant primer regions.
Format Flexibility: Offering DNA, RNA, or modified nucleotide (e.g., 2′-F, 2′-O-Me) libraries to balance stability, cost, and affinity requirements.
Target Immobilization: A critical initial step where the small molecule target is conjugated to a solid support (beads, column) or a tag (biotin) to facilitate separation during screening.
This is the core iterative cycle, refined for efficiency and stringency:
Binding & Partitioning: Incubation of the library with the immobilized target. Weak or non-binders are washed away. Stringency is increased over rounds (e.g., by adding competitors or reducing incubation time).
Elution & Recovery: Specifically bound sequences are eluted, often by disrupting the aptamer-target interaction.
Amplification: Eluted sequences are amplified by PCR (for DNA) or Reverse Transcription-PCR (for RNA).
Counter-Selection (Negative Screening): A critical step to ensure specificity. The enriched pool is passed against a negative control (e.g., the immobilization matrix alone or a related molecule) to subtract non-specific binders.
Monitoring & Iteration: The process is repeated for 8-15 rounds, with binding affinity monitored after each round (e.g., via qPCR or flow cytometry). High-Throughput Sequencing (HTS) is typically performed on key rounds to identify enriched sequence families.
This phase transforms candidate sequences into validated, usable reagents:
Bioinformatics Analysis: Analysis of HTS data to identify consensus motifs, cluster families, and select lead candidates for synthesis.
Affinity & Specificity Characterization: Determination of dissociation constant (Kd) using techniques like Surface Plasmon Resonance (SPR), Bio-Layer Interferometry (BLI), or Isothermal Titration Calorimetry (ITC). Cross-reactivity tests against structural analogs.
Aptamer Optimization: Truncation studies to identify the minimal binding domain, and chemical modifications to enhance nuclease resistance and serum stability.
Functional Validation: Testing the aptamer’s performance in the intended application (e.g., as a biosensor component, inhibitor, or targeting agent in a diagnostic assay).
Proprietary Methods: May include advanced SELEX variants like Capture-SELEX (for unmodified small molecules), CE-SELEX (for superior partitioning), or Cell-SELEX (for complex targets).
Integrated Platform: Combines molecular biology, high-throughput sequencing, and biophysical analytics under one roof.
Project Customization: Service is tailored based on the client’s target, desired aptamer format (DNA/RNA/modified), and end-use application.
In summary, KMD Bioscience’s service provides an end-to-end solution, translating a small molecule target into high-affinity, specific aptamers ready for downstream development in diagnostics, therapeutics, and biotechnology.

Aptamer Affinity Optimization

Aptamer Library Construction

Customized Aptamer Selection

High-throughput Aptamer Screening

High-Throughput Sequencing SELEX Aptamer Screening Service

Conventional SELEX Aptamer Screening Service

Negative SELEX Aptamer Screening Service

Toggle-SELEX Aptamer Screening Service

Capture-SELEX Aptamer Screening Service

Surface Plasmon Resonance SELEX Aptamer Screening Service

Capillary Electrophoresis SELEX Aptamer Screening Service

Magnetic Bead-based SELEX Aptamer Screening Service

Toggle-SELEX Aptamer Screening Service

Negative Aptamer Selection- A Practical Guide to Improving Aptamer Specificity in SELEX

selexkmdbio-Cell Nucleic Acid Aptamer Screening Service

Aptamer Screening- Current Methods and Future Trend towards Non-SELEX Approach

Aptamer Screening Service-Subtractive SELEX

Aptamer Screening Service-Counter SELEX

Aptamer Screening Service-HT-SELEX

Aptamer Screening Service-NGS-SELEX

Aptamer Screening Service-Multi-Round SELEX Screening

Whole Cell-SELEX Aptamer Screening Service

Membrane Protein Aptamer Screening Service

Aptamer Screening Service for Drug Discovery

Aptamer Live Cell SELEX Service

Classical SELEX Service for Aptamer

Aptamer Selection and Identification

Aptamer Screening Process and Applications Overview